We have seen people forgetting the names of their families and friends, dates, and days. On the other hand their ability to reason and think started declining majorly, and they often found it difficult to perform basic daily tasks—all of these mark the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
What is Alzheimer’s Disease?
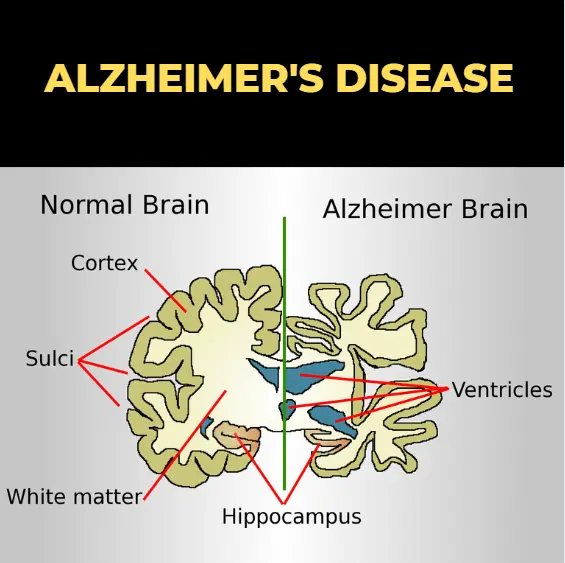
This disease is a neurological disorder that affects the brain and causes it to shrink, resulting in the death of some brain cells. The disease that many people suffer from affects the ability to carry out tasks and think independently. however social and physical skills decline, resulting in their dependence on the people surrounding them, like family and friends.
Why is it Called Alzheimer’s Disease?
The name Alzheimer’s is given to this disease after Dr. Alois Alzheimer. In 1906, a woman died, and the reason for her death was a mystery illness that was unknown to the world of medicine. She showed symptoms of memory loss, language issues, and unexpected behavioral patterns. In this case unusual cause of her death led Dr. Alois Alzheimer to study her brain. He found some clumps(amyloid plaques) and bundles of fibers (neurofibrillary or tangles) tangled together. Thus, he discovered th and worked further to know more about it and how it affects a person throughout their Alzheimer’s journey.
Symptoms of Alzheimer’s
Our brain becomes incapable of performing complex functions, which give rise to the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. They include;
- Memory loss
Loss of memory is one of the initial symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. Thus person starts forgetting simple things like events, dates, something they’ve kept somewhere. They often forget the places they’ve been familiar with and find it too hard to remember the names of some objects. The inability to remember things and events worsens over time, followed by other major symptoms.
- Thinking and Reasoning
People with Alzheimer’s disease face difficulties in reasoning, thinking, and understanding abstract concepts. Secondly they often face difficulty in recognizing numbers and letters. Their ability to make decisions and reason suffers too.
- Performance of Basic Tasks
People with Alzheimer’s disease often forget how to perform basic daily tasks like eating, changing clothes, taking showers, etc. On the other hand they often lose the ability to plan and carry out sequential tasks like playing chess, organizing a cupboard, or cooking.
- Personality and Behavioral Changes
The brain of an Alzheimer’s patient doesn’t function normally. They face difficulties and hindrances in their lives due to the drastic change in their brain’s alchemy. They also show changes in their personality and behavior as their emotions become out of control. The issues might include,
- Inability to trust others.
- Depression
- Anxiety
- Changes in mood
- Delusions
- Social withdrawal
Causes of Alzheimer’s Disease
There is not enough evidence on the causes of this disease. But, a study has proven that abnormalities in brain function cause this disease. It happens during old age after the person turns 65.
When we talk about brain function, Alzheimer’s patients experience a kind of protein build-up in and out of their brain cells. One of them is called amyloid, which results in the formation of clumps – plaques– around the brain cells.
There is another protein, known as tau, when building up in excess, results in tangles in the brain cells.
The protein build-up is what paves the way toward Alzheimer’s disease. But, the cause of such complex abnormalities is unknown.
We know that our brain cells play an essential role in sending signals efficiently. But when they’re affected, there is a decline in the activity of neurotransmitters.
Some factors might manifold the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
- Family History
- Age
- Head injury
- Cardiovascular disease
- Down Syndrome
- Mild Cognitive Impairment
Preventative Measures
Well, Alzheimer’s disease is not something preventable. But, we can take measures to modify and incorporate some healthy physician habits. Research has proved that eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a distance from cardiovascular disease, can reduce the risk of developing this disease. Other than these preventive steps, the person experiencing the symptoms should be taken immediately to the doctor for initial evaluation.